Human ancestors went from Africa to the world
Advertisement
Modern humans first appeared in sub-Saharan Africa about 200,000 years ago. For a long time, there has been much controversy about the timing and process by which modern humans crossed the Sahara and made their way out of Africa. Previous studies have suggested that modern humans moved out of Africa on a large scale between 70,000 and 40,000 years ago. However, a recent study suggests that modern humans may have started their journey to the world as early as 130,000 years ago, and subsequently expanded out of Africa several times.

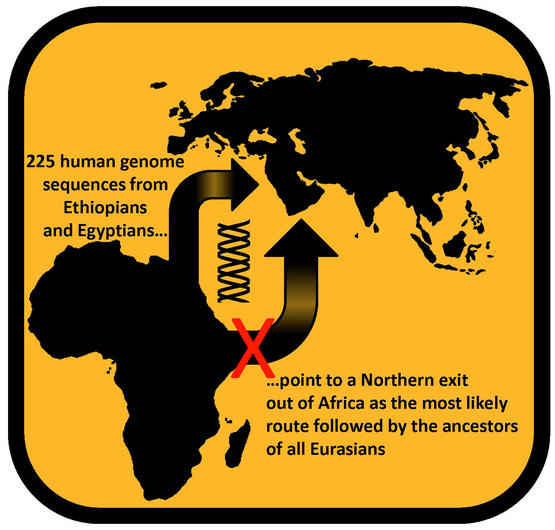
Scientists used to believe that modern humans had two routes out of Africa. One, known as the northern route, saw humans leave Africa through what is now Egypt and the Sinai Peninsula; the other, known as the southern route, saw humans leave from what is now Ethiopia and the Arabian Peninsula. Both migratory routes lack adequate and reliable evidence.
Advertisement
To figure out which route modern human ancestors might have taken when they left Africa, the researchers sequenced the genomes of 225 people (Including 100 Egyptians and 125 Ethiopians) in northeastern Africa. They then matched these data with East Asians (Specifically Han Chinese), South Asians (Gujaratis in India), and Europeans (Tuscans in Italy), respectively. In addition, they matched the data with modern sub-Saharan West Africans whose genes can broadly reflect the gene pool of ancient sub-Saharan humans.
The scientists noted that modern Egyptians and Ethiopians have recently experienced a history of migration from outside Africa, and the resulting mixing may have increased the genetic similarity between them and those who moved to Africa. With this in mind, the researchers eliminated all genetic sequences that could have come from recent immigrants.
Advertisement
- Previous article
- Georgina is wearing Dior and slippers
- Next article
- How can we set and remember easy-to-remember but hard-to-guess passwords?
Advertisement
OTHER NEWS

Does Eating Lunch at Your Desk Make you Feel Stressed
BY Lillian

Make cos clothes out of waste fabric materials
BY Ann

Social methods: The phone calls make us feel better than text communicating
BY Diana

The largest mammoth fossil has been discovered in Mexico
BY Sandra

Listening Mozart music can help epilepsy?
BY Lisa
When do we reach our peak brain power?
BY Lisa
RECENT NEWS
-

PUBG Mobile Esports Generated 200 Million Hours of Viewing in 2020
-

Mario Kart Tour Races to $200M revenue and 200M Downloads
-

Game Acquisitions Expand Globally in Q1 2021 with 280 Deals Worth $39 Billion Surpassing That in 2020
-

Free Fire Shows Strong Momentum, with Its Revenue Overtaking PUBG Mobile in a Single Market for Q1 2021
-

The Games Fund Launched a $50 Million Early Investment Fund to Invest in American and European Companies
-

How to Download and Install Wyze App for Free?
 1
1 1
1